Consistent Protection after Knee Replacement Surgery, Evidenced in Clinical Studies,1,2 Reaffirmed in the Real-World3
Prevention of VTE after elective knee replacement surgery
The first approved indication4 for Xarelto® was for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in adults undergoing elective knee replacement surgery
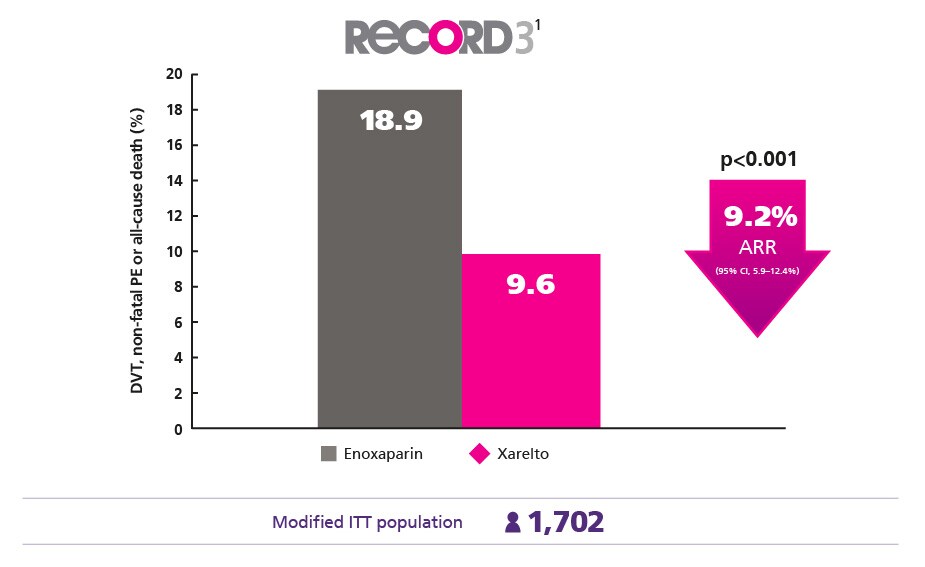
Superior Protection for Your Elective Knee Surgery Patients1
Provide better protection against DVT , nonfatal PE and death from any cause vs enoxaparin
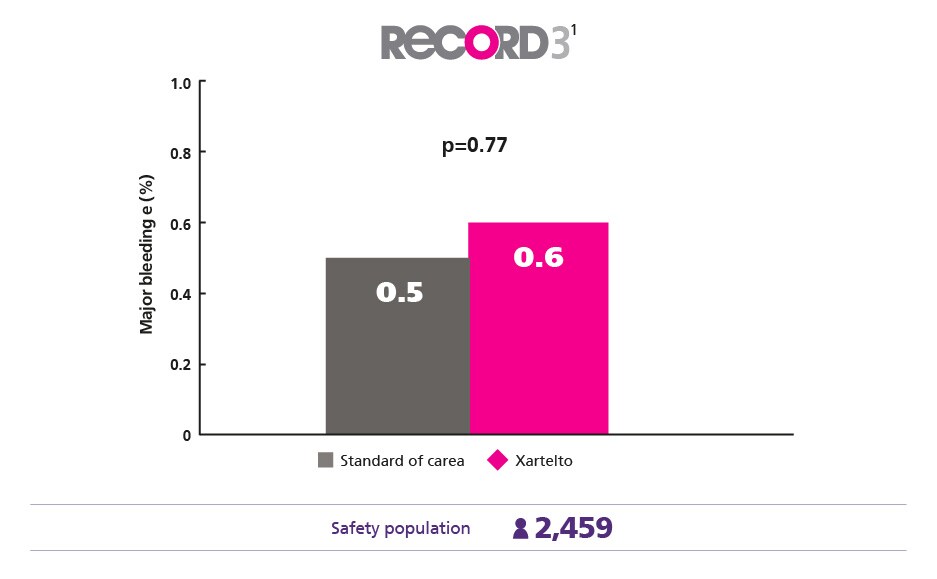
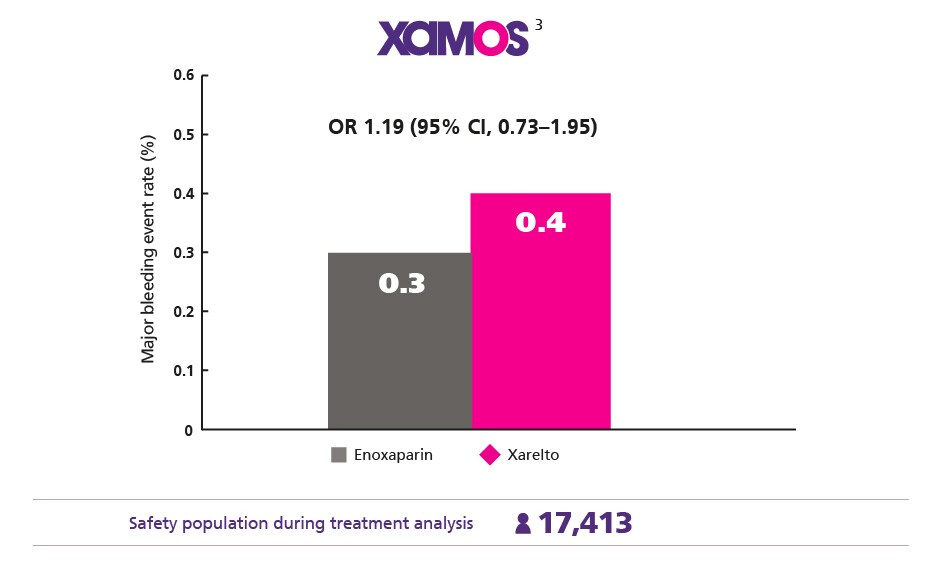
Comparable Safety Profile1
Maintain a low major bleeding rate vs enoxaparin
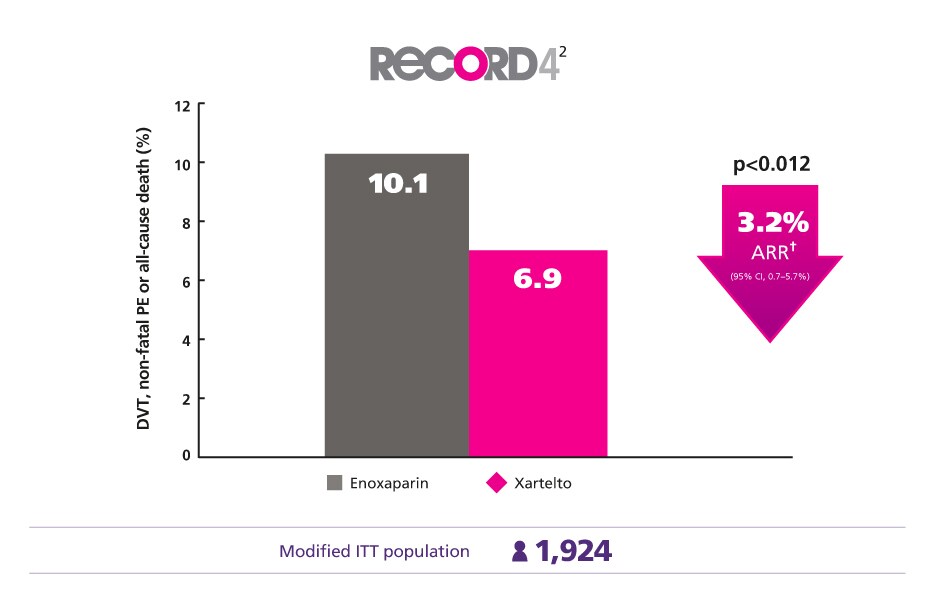
Effective Thromboprophylaxis Achieved with Less Medicinal Treatment2
Better protect your patients with less medicinal treatment vs enoxaparin
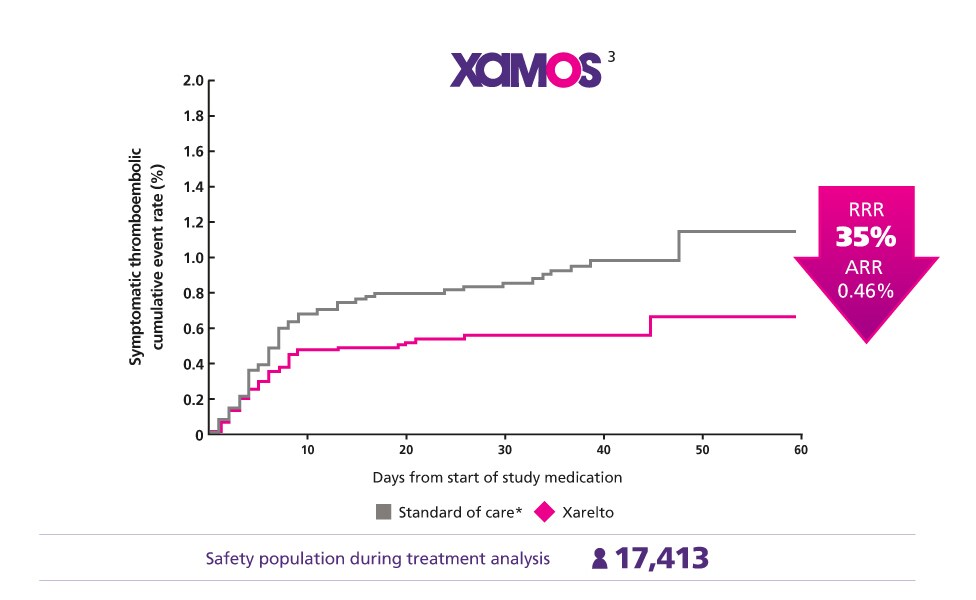
Consistent Protection Confirmed in the Real World3
Give your everyday patients the consistent protection they need
ARR, absolute risk reduction; CI, confidence interval; DVT , deep vein thrombosis ; ITT , intention-to-treat; LMWH , low-molecular-weight heparin; OD, once daily; OR, odds ratio; PE , pulmonary embolism; RRR , relative risk reduction; VTE , venous thromboembolism.
PP-XAR-ALL-1794-1
References
- Eriksson BI, et al. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2765–2775. Eriksson BI, et al. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2765–2775. Return to content
- Kakkar AK, et al. Lancet. 2008:372:31–9. Return to content
- Turpie AG, et al. Thromb Haemost. 2014;111:94¬–102.. Return to content
- Xarelto (rivaroxaban) Summary of Product Characteristics. Xarelto (rivaroxaban) Summary of Product Characteristics. Return to content
RELATED PODCAST
CAD or symptomatic PAD discussion