Prevention of Atherothrombotic Events in Peripheral Artery Disease
Prevention of Atherothrombotic Events in Peripheral Artery Disease
Xarelto is indicated for the prevention of atherothrombotic events in adults with symptomatic peripheral artery disease (PAD) at high risk of ischaemic events.1
Protection starts with getting to know your patient
How do you protect your patients like Roberto?
What does the future look like for your patients after revascularisation?
Are you aware of the risks your patients face?
Improve the outcomes that matter most for patients like Roberto
What does long-term protection look like to you?
How many could benefit?
See how your patients could benefit from the protection you provide
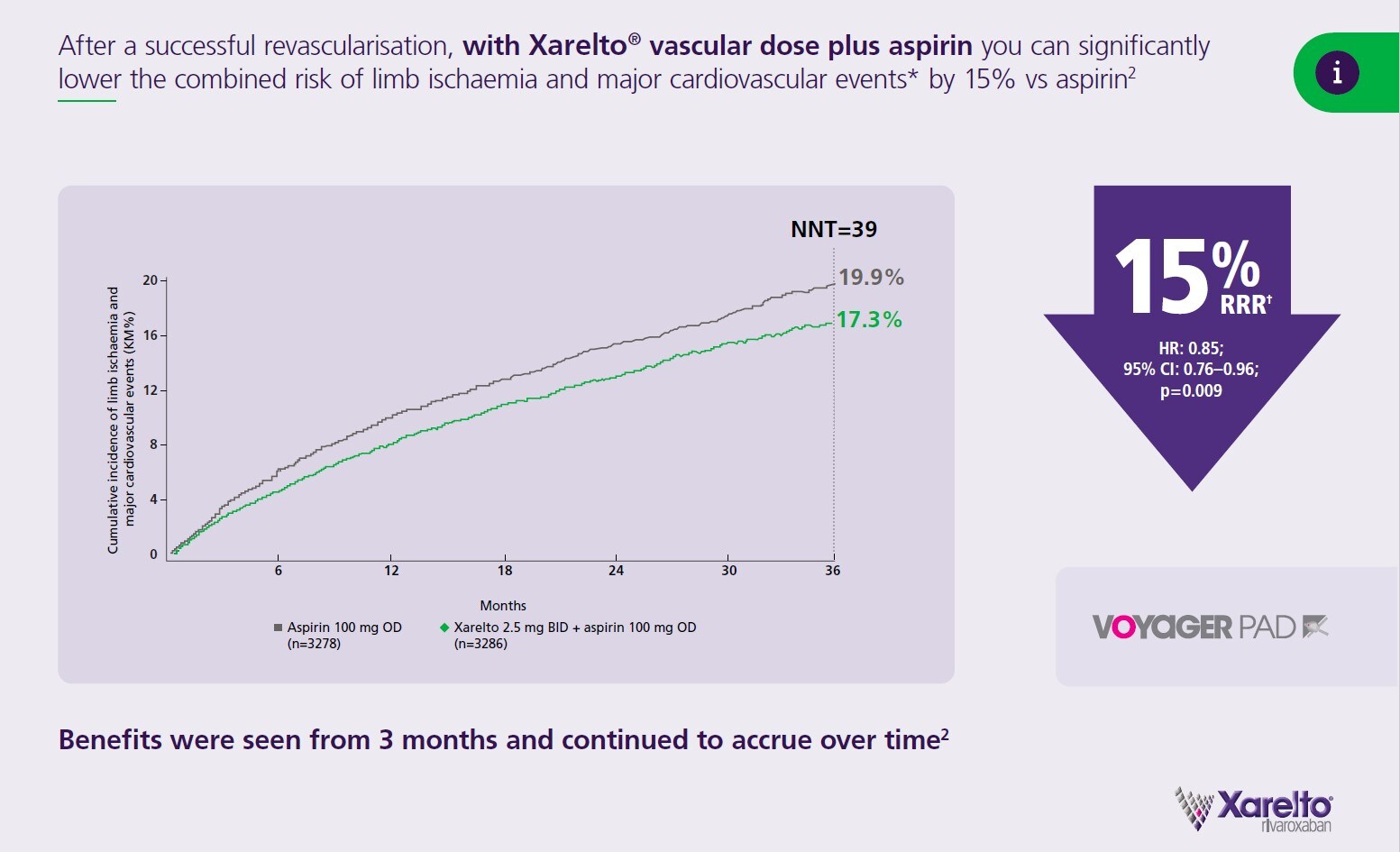
Protection for your patients continues immediately after revascularisation
Protect your patients against major adverse vascular events
BID, twice daily; CI, confidence interval; HR, hazard ratio; MI, myocardial infarction; NNT, number needed to treat; OD, once daily; PAD, peripheral arterial disease; RRR, relative risk reduction
PP-XAR-ALL-2120-1
References
- Bayer AG. Xarelto® (rivaroxaban) Summary of Product Characteristics. Available at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/documents/product-information/xarelto-epar-product-information_en.pdf. Bayer AG. Xarelto® (rivaroxaban) Summary of Product Characteristics. Available at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/documents/product-information/xarelto-epar-product-information_en.pdf. Return to content
- Bonaca MP, et al. N Engl J Med 2020;382(21):1994–2004 Return to content
- Aspirin Summary of Product Characteristics. Available at: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/4172/smpc. Aspirin Summary of Product Characteristics. Available at: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/4172/smpc. Return to content
RELATED PODCAST
CAD or symptomatic PAD discussion